JupyterHub Integration
Accessing JupyterHub

- Clicking
Services > JupyterHubon the left-hand toolbar starts an OAuth2.0 workflow to access the JupyterHub hosted on your compute cluster. - Click on the “Sign in with Kaspian” Button
- Wait for the JupyterHub service to spin up (this may take up to several minutes).
- The web page should automatically redirect to a familiar JupyterLab workspace UI.
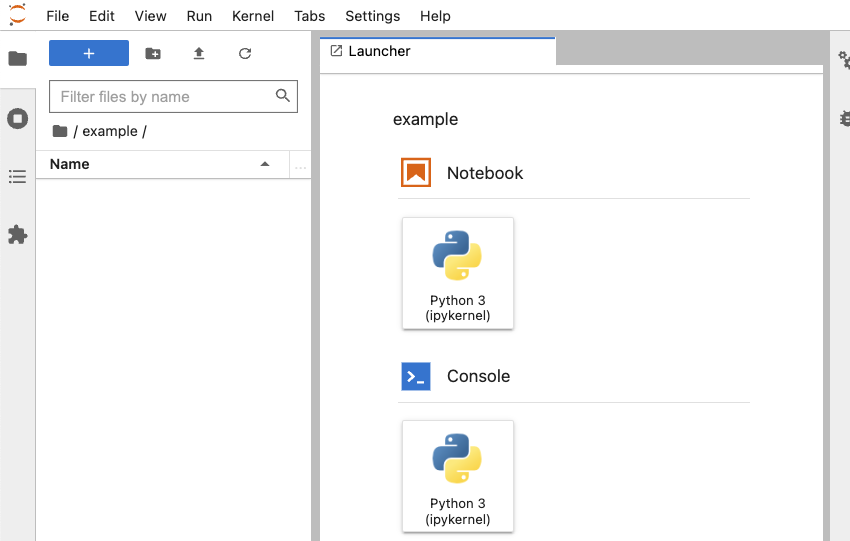
Using JupyterHub
JupyterHub documentation mostly concerns the JupyterHub deployment process. For tips on using JupyterHub, we recommend looking at the JupyterLab documentation here.
JupyterHub Control Panel
The Hub Control Panel allows access to a JupyterHub server’s management options. Access the Hub Control Panel via the JupyterHub toolbar with File -> Hub Control Panel, which will launch the page below:
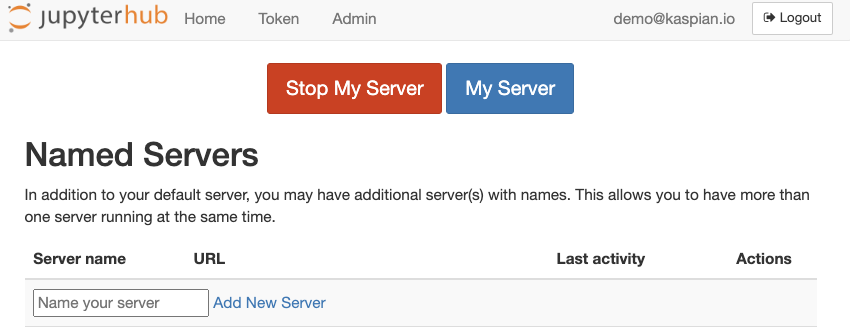
Named Servers
Kaspian’s hosted JupyterHub service provides an option for a single user to run multiple servers, which may be useful for simultaneously running computationally-intensive tasks. Named Servers can be launched and managed via the Hub Control Panel described above.
Note
Server names must consist of alphanumeric characters,_, -, or .Manual Shutdown
Shutdown the JupyterHub server manually by navigating to the Hub Control Panel. Click on the “Stop My Server” button to stop the server, and optionally “Logout” to log out of JupyterHub.
Note
Because JupyterHub servers are backed by cloud compute instances, keeping them running for long periods of time can increase costs. The Kaspian team therefore recommends manually shutting down servers expeditiously. JupyterHub will persist any saved files or notebooks, so all data will be re-accessible when the server restarts.Automatic Shutdown
JupyterHub servers idle (no kernels actively running user code) for longer than 1 hour will be automatically shut down to conserve compute for other users. This is a configurable parameter; to change this timeout threshold, please contact Kaspian support.
Accessing other services running in JupyterHub
Kaspian’s hosted JupyterHub services comes pre-installed with the Jupyter Server Proxy, which allows running arbitrary external processes alonside a notebook server, and accessing them via a web URL path based on the JupyterHub server’s URL.
In general, services running locally in a JupyterHub server located at:https://jupyterhub.example-company.kspn.io/user/demo@example-company.com/
should be accessible at:https://jupyterhub.example-company.kspn.io/user/demo@example-company.com/proxy/<service_port_number>
For example, when running a spark session spark locally in a JupyterHub server notebook, the Spark UI can be accessed at https://jupyterhub.example-company.kspn.io/user/demo@example-company.com/proxy/4040/jobs/.